Orthognathic surgery is used to surgically correct jaw and facial skeletal deformities. During the growth process of the lower and upper jaws, they grow forward and downward in harmony with each other. Growth and development are predominantly affected by genetic factors or, less frequently, by environmental factors. Skeletal deformities occur as a result of negative effects on growth and development. These disorders can be in various clinical forms such as lower jaw positioning more forward than normal, and upper jaw positioning further back than normal.
Although growth and development disorders of the jaw and face are observed at earlier ages, conventional preventive or directive treatments may not be successful. By the end of growth and development, the treatment of skeletal disorders will only be possible with surgical treatment.
Upper and lower jaw teeth often show different alignments in order to tolerate the functional problems caused by jaw deformities. For this reason, orthodontic treatment before the surgical treatment of jaw deformities ensures that the teeth are positioned where they should normally be. Otherwise, incompatible closure of the teeth after surgery is encountered.
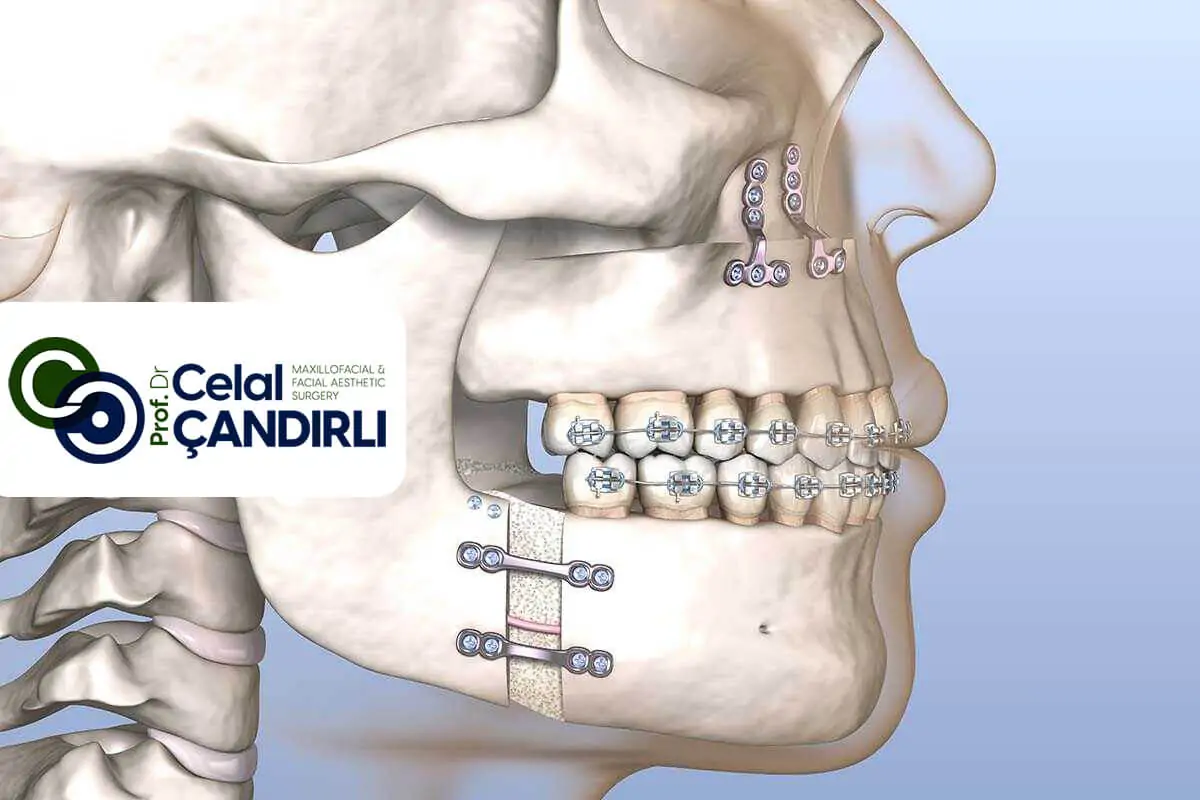
After orthodontic treatment, skeletal disorders are corrected by surgery. There are many surgical techniques applied on the lower and upper jaw. The most commonly applied techniques are Le Fort 1 Osteotomy – Down Fracture in the upper jaw and Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy in the lower jaw. With these techniques, the lower and upper jaws are brought to the required position with three-dimensional movements and fixed in their new positions with titanium plates and screws.
Surgical procedures take between 2 and 4 hours, depending on whether it is a single jaw or a double jaw. It is often applied with nasal intubation technique under general anaesthesia. The patient who has the surgery stays in the hospital for 1 or 2 days and rests at home for about 1 week. The muscles attached to both the upper jaw and the lower jaw want to return to their former state, and guiding elastics can be attached to the lower and upper jaws after surgery in order to prevent the forces exerted by the muscles. Contrary to popular belief, it is unnecessary to bind the jaws tightly after surgery and patients can be fed with normal soft foods.
2 weeks after the surgical intervention, patients return to their normal lives to a large extent and continue their orthodontic treatment. Patients are fed soft foods for 1 to 3 months after the operation, and then they can start to take hard foods.
Prof Dr. Celal Çandırlı performs Orthognathic surgery in our clinic located in Istanbul, Turkey. Dr. Celal Çandırlı has experience of more than two thousand orthognathic surgery cases. All other aesthetic and functional jaw surgery operations are performed in our clinic.
NUTRITION AFTER ORTHOGNATIC SURGERY
If the doctor who performs the orthognathic surgery is experienced, the post-operative process will be much more painless and easier because orthognathic surgery is a technical operation and a mistake made while fixing the bones will cause serious problems.
In orthognathic surgery applied on the upper jaw, bone incisions are made through the mouth and no incision is made on the skin. To reach the bone, a soft tissue incision is made through the mouth under the upper lip. Bone incisions are made from the right and left of the nasal cavity to the back, at least 5 mm above the roots of the teeth. After the incisions are made, the upper jawbone is mobilized. The mobilized bone piece is placed in its new position with orthognathic surgical splints. During this procedure, an experienced surgeon makes the bone mobile easily and most importantly, it does not disturb the nutrition of the bone while doing these. Otherwise, bone necrosis may occur after surgery, which is a serious complication. The surgeon fixes the upper jaw in its new position with titanium mini plates.
Although the surgery of the lower jaw is technically easier than the surgery of the upper jaw, the biggest reason for postoperative failures is the mistakes made in the lower jaw surgery. Especially if the original position of the jaw joint is deteriorated while the bones are fixed in their new position, the jaws will not return to the desired position after the surgery and the surgery will fail. Inexperienced surgeons often change the location of the condyle at this time and the jaws are not in the desired position after the operation.
Many surgeons forcibly fix the lower and upper jaws with elastics to solve this problem. This process can cause serious damage to the joints. The surgeon who makes a mistake applies this procedure for almost 1 month and may cause permanent damage to the joint. At the same time, patients experience serious weight loss as they cannot be fed during this period, and this causes both physiological and psychological damage to the patient.
If the position of the jaw joint is maintained during the fixation of the lower jawbone, there is no need for post-operative elastic fixation of the jaws. Guiding elastics are used only to prevent the pulling of the muscles, but this does not prevent the patient from feeding.
In orthognathic surgery, the jaws are broken and repositioned. For this reason, actions that will impair the healing of bone fractures after surgery should not be taken. For example, it is recommended that patients be fed with soft foods such as soup and mashed potatoes for the first month. One month after the surgery, you can start eating home-made meals such as pasta. 3 months after the surgery, bone healing is completed to a large extent and the patient can start eating harder foods. Protein-rich foods can be preferred to ensure healthy post-operative bone healing. In this process, oral care must be done well, otherwise tooth decay and gum diseases may begin. For this reason, it would be right to stay away from sugary foods during the postoperative period. After a correct operation, the teeth can be easily brushed. This process does not damage the sutures in the mouth, but it will be more correct to use soft brushes.
Feeding with a straw after surgery is never correct. Because after a correctly performed surgery, there is no need to tie the jaws with elastic and there is no need to feed with a straw.
Does lip numbness occur in orthognathic surgery?
The head and neck region are the most anatomically complex region of the body. Vessels and nerves run like cables from the base of the skull to the face, neck, and body. There are passage routes of vessels and nerves in the lower and upper jaw. In particular, the nerve called the Alveolaris inferior passes through the lower jawbone and provides the sensation of the lip. In orthognathic surgery, bone incisions are made in the lower and upper jaw and the bones are positioned from their original places to their planned places. For this reason, the nerve in the lower jaw may be damaged during bone incision or may be stretched during the movement of the jaw. Therefore, the nerve may not function temporarily. This may result in a decrease in the patient’s lower lip sensation clinically. If the nerve is not damaged during surgery and is only slightly affected by tension or post-operative oedema, this numbness is temporary and usually improves greatly within 3 to 6 months. If the nerve is severely damaged during surgery, the nerve should be repaired with microsurgery during the operation. If necessary, nerve grafts should be taken from different parts of the body.
In the upper jaw, the nerve that provides the sensation of the upper lip may be affected, although rarely, and upper lip numbness may be observed after surgery. But upper lip numbness heals much faster within weeks.
It is very important that experienced teams in orthognathic surgery perform the operation. Many of the complications experienced in surgery are due to inexperience.