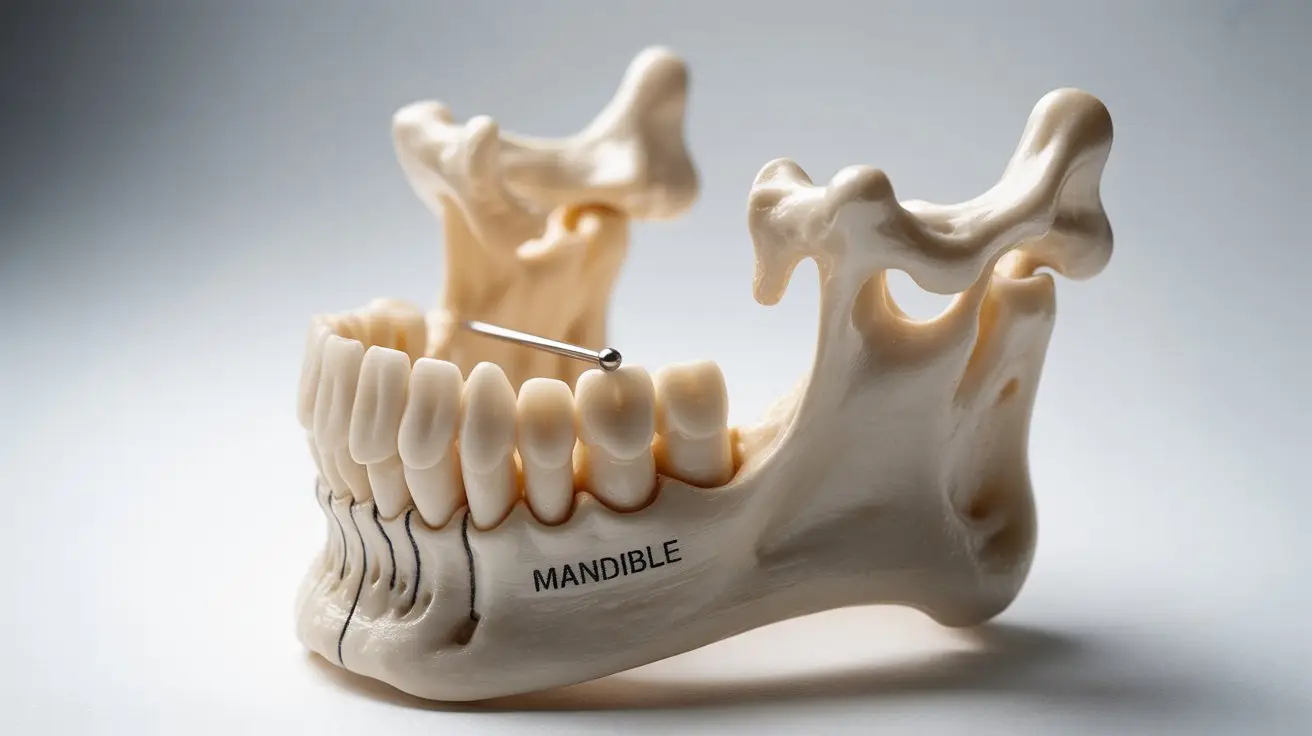
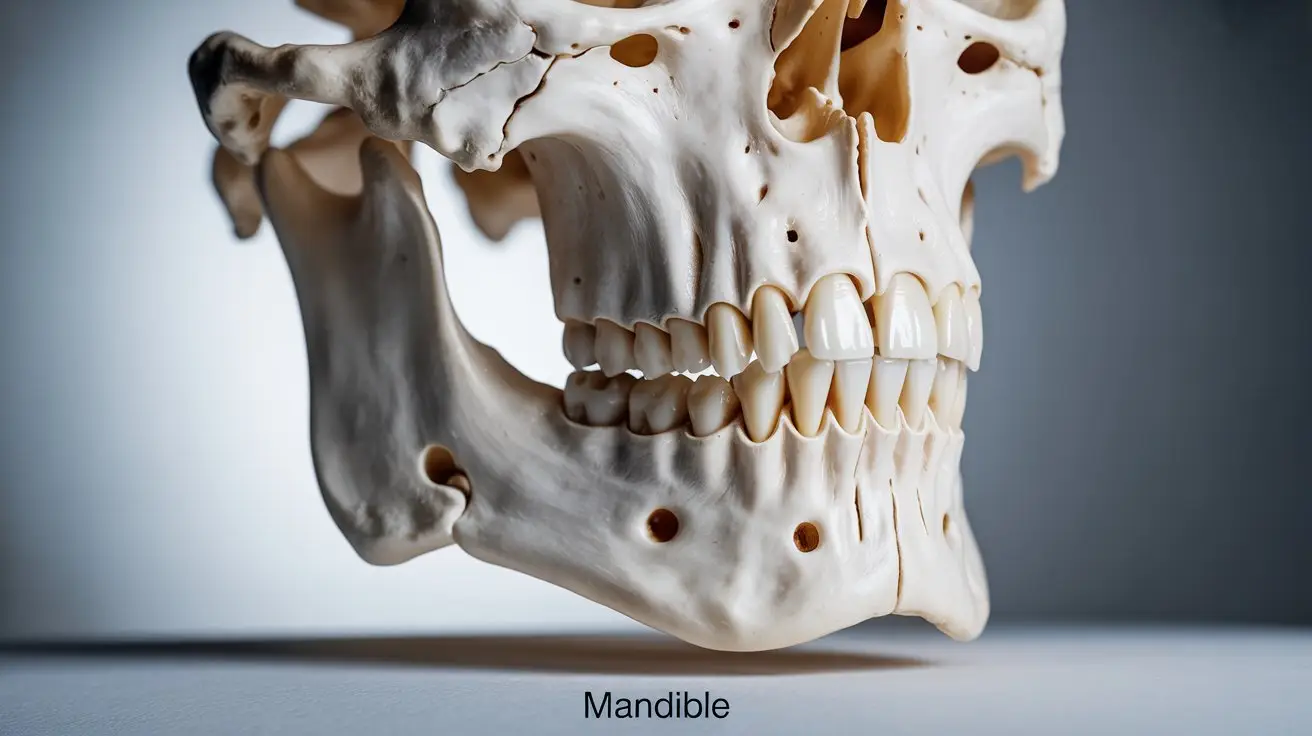
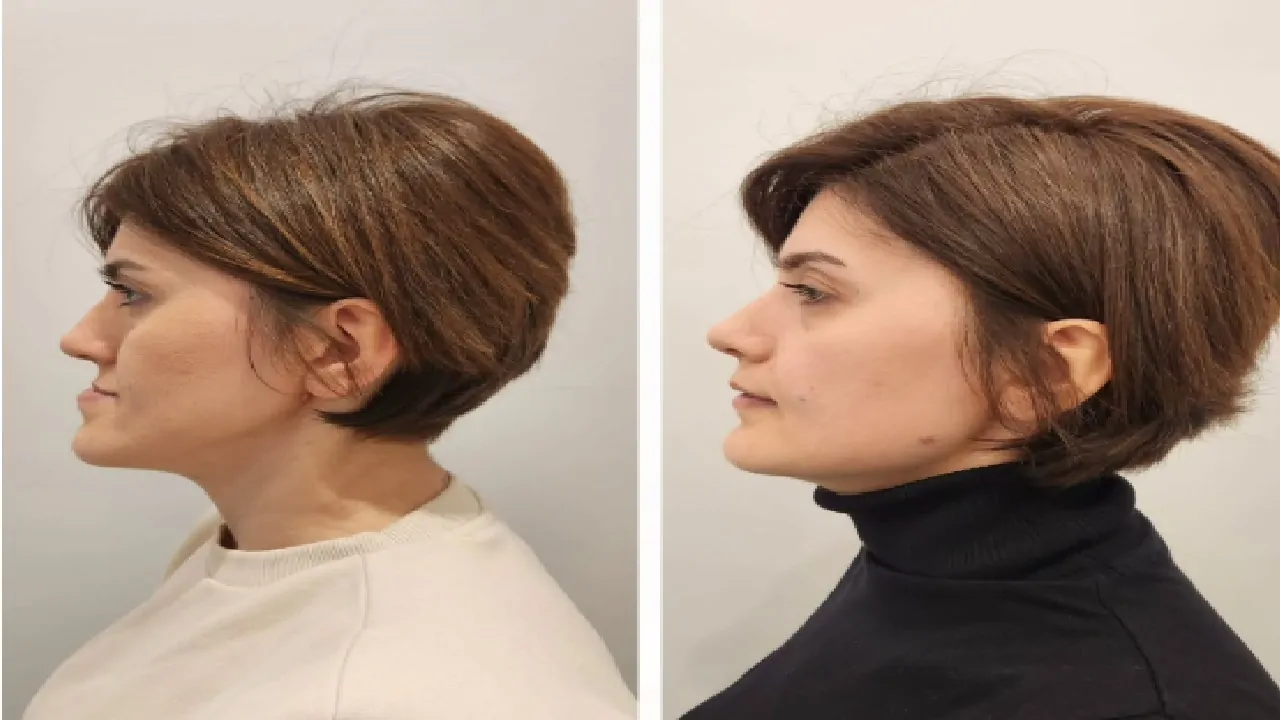
The jaw bone mandible, also known as the mandible, is one of the most important structures in the human face. It provides shape, balance, and functionality by supporting the lower teeth and enabling essential movements such as chewing, speaking, and facial expression.
Any misalignment, deformity, or trauma involving the mandible can affect both oral health and overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the anatomy and functions of the jaw bone mandible, common conditions that affect it, and how surgical interventions by experts like Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı can restore both function and aesthetics.
Anatomy of the Jaw Bone Mandible
The mandible, or lower jawbone, is the most robust and substantial bone in the human face. Unlike the fixed upper jaw (maxilla), the mandible is capable of movement and articulates with the skull via the temporomandibular joints (TMJ).
Key Features of the Jaw Bone Mandible
The jaw bone mandible consists of several key structures, each playing a vital role in both function and appearance. From holding the lower teeth in place to enabling smooth jaw movement, these features work together to support chewing, speaking, and facial aesthetics. Understanding the main components of the mandible is essential for recognizing how surgical or corrective treatments can improve both health and appearance.
| Mandible Part | Function / Role |
| Body of the Mandible | Holds the lower teeth in position and supports chewing. |
| Ramus | Vertical portion that connects the mandible to the skull. |
| Chin (Mental Protuberance) | Shapes the lower face, contributing to facial aesthetics. |
| Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) | Enables jaw movement for chewing, speaking, and expression. |
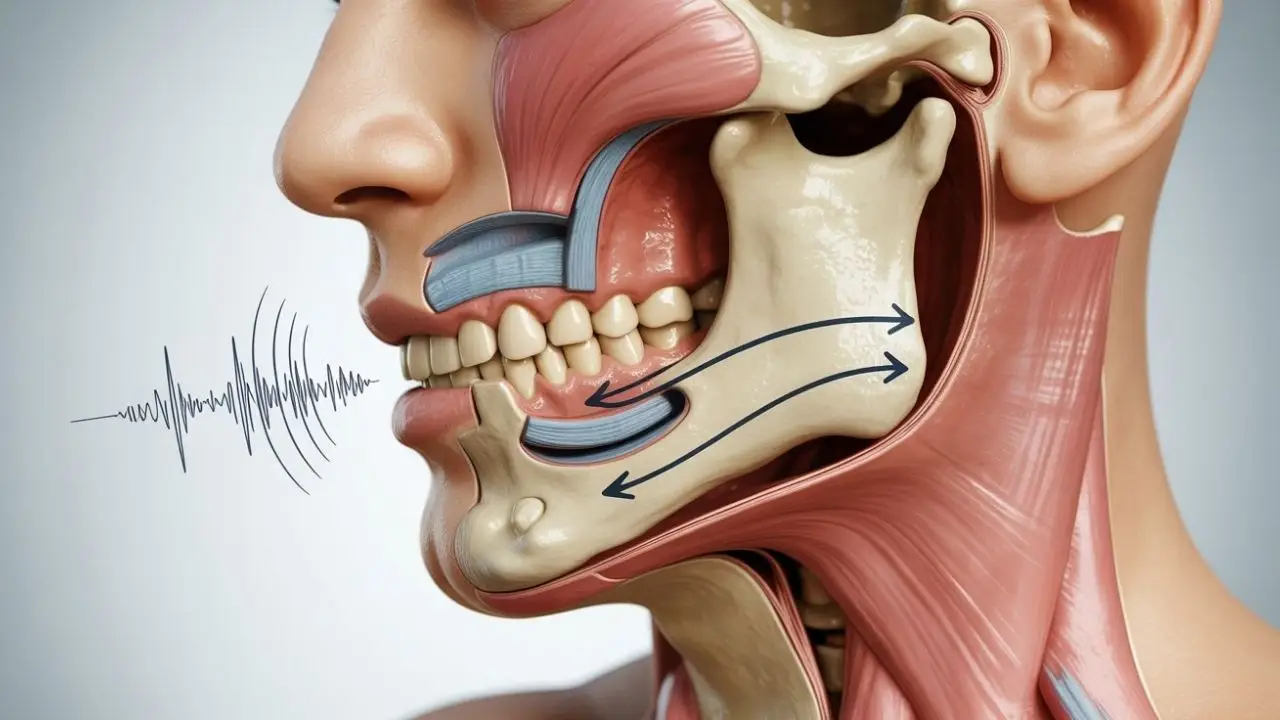
Functions of the Jaw Bone Mandible
The jaw bone mandible is a key component of both function and facial aesthetics. It not only enables essential activities like chewing and speaking but also supports the overall structure and balance of the lower face. Proper alignment and health of the mandible are crucial for efficient mastication, clear speech, and a harmonious facial appearance. Understanding these functions highlights why maintaining or correcting mandible health is so important.
1. Mastication (Chewing)
The mandible works closely with the maxilla to break down food efficiently. Proper jaw function ensures that chewing is smooth and effective, aiding digestion. Any misalignment or dysfunction of the mandible can lead to difficulty in eating and nutritional issues.
2. Speech
A properly aligned jaw bone is essential for clear pronunciation and effective communication. The mandible’s movement helps form words and control airflow during speech. Jaw disorders or misalignments can cause slurred speech or difficulty articulating certain sounds.
3. Facial Structure
The mandible plays a crucial role in defining the lower face and overall facial symmetry. Its shape influences the jawline, chin, and profile, impacting appearance and attractiveness. Correcting mandible alignment can enhance both aesthetics and self-confidence.
Common Conditions Affecting the Jaw Bone Mandible
The jaw bone mandible plays a vital role in daily functions such as chewing, speaking, and maintaining facial balance. However, various medical and dental conditions can affect its structure and performance, leading to discomfort or aesthetic concerns. From misalignment and TMJ disorders to trauma and congenital issues, understanding these common problems is essential for determining the right treatment and achieving long-term oral health.
Jaw Misalignment
Jaw misalignment occurs when the jaw bone mandible does not properly align with the upper jaw. This condition can lead to bite problems such as overbite, underbite, or crossbite. If left untreated, it may cause difficulties in chewing, speaking, and overall facial balance.
TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders involve dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint that connects the mandible to the skull. Patients often experience jaw pain, clicking sounds, or restricted movement. In severe cases, it can interfere with daily activities like eating and speaking.
Trauma or Injury
The jaw bone mandible is highly vulnerable to trauma, especially in accidents or sports injuries. Fractures and dislocations can disrupt both function and appearance. Surgical treatment is often required to restore proper alignment and stability.
Congenital or Developmental Issues
Some individuals are born with congenital deformities affecting the mandible’s growth. These developmental issues may cause facial asymmetry, misaligned teeth, or breathing problems. Corrective surgery is often the most effective solution for long-term improvement.
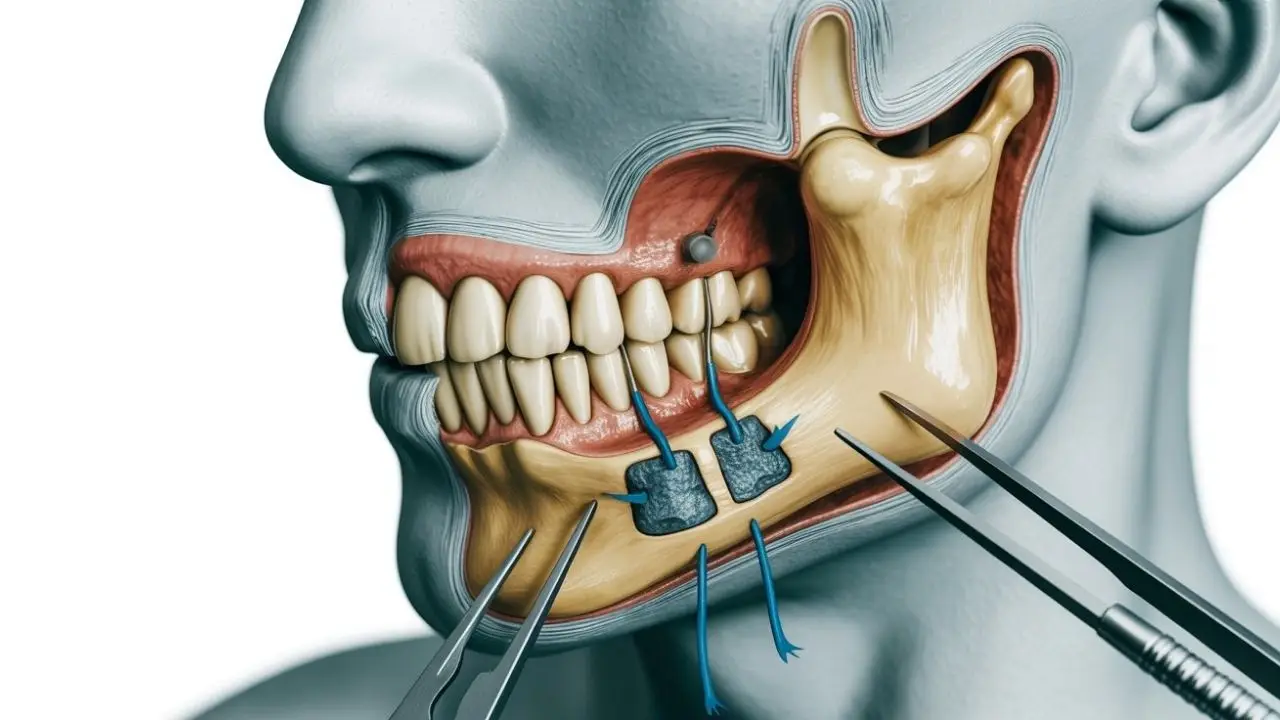
Surgical Solutions for Mandible Problems
When orthodontic treatment alone cannot resolve severe discrepancies, jaw surgery (orthognathic surgery) becomes the best option.
Benefits of Mandible Surgery
- Restores proper bite function
- Improves facial harmony and jawline aesthetics
- Relieves TMJ-related pain and discomfort
- Enhances breathing and airway function
Why Choose Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı for Jaw Bone Mandible Surgery?
With decades of expertise in maxillofacial and orthognathic surgery, Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı is a trusted authority in treating complex mandible-related conditions. His patient-centered approach, advanced surgical planning techniques, and proven success in double jaw and mandible surgeries make him a preferred choice for both local and international patients.
Learn more about his innovative treatments and success stories at 👉 celalcandirli.com.
Frequently Asked Questions
The jaw bone mandible plays a vital role in both function and appearance, impacting chewing, speech, and facial aesthetics. When problems arise due to misalignment, trauma, or congenital issues, surgical intervention offers life-changing results. With the expertise of Prof. Dr. Celal Çandırlı, patients can achieve lasting improvements in oral health, facial harmony, and quality of life.
Are the Mandible and Jaw Bone the Same?
The mandible is commonly referred to as the lower jaw bone, so in everyday language they are often used interchangeably. However, anatomically speaking, the term “jaw” can include both the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower jaw (mandible). The mandible is the only movable bone of the facial skeleton.
Why Does My Mandibular Jaw Hurt?
Pain in the mandible can be caused by muscle strain, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, dental infections, trauma, or nerve irritation. Clenching or grinding teeth, stress, and poor posture can also place extra strain on the mandible. Persistent or worsening pain should be medically evaluated.
What Is Another Name for the Mandible?
Another commonly used name for the mandible is the lower jaw. In medical and anatomical contexts, the term “mandible” is preferred because it precisely identifies this specific bone.
Why Do I Feel a Little Ball in My Jaw?
A small lump or “ball” sensation in the jaw may be due to a swollen lymph node, muscle knot, salivary gland issue, or localized inflammation. In some cases, it can also be related to dental infections or cysts. If the lump persists, grows, or becomes painful, professional evaluation is recommended.
How Painful Is Mandible Surgery?
Mandible surgery is performed under anesthesia, so pain is not felt during the procedure. After surgery, discomfort and swelling are expected but are usually manageable with prescribed pain medication. Pain levels vary depending on the type and extent of surgery.
Why Is It Called a Mandible?
The word “mandible” comes from the Latin term mandibula, which means “to chew.” This name reflects the bone’s primary function in chewing, biting, and supporting lower teeth.
Can Sleeping Position Affect Jaw Pain?
Yes, sleeping position can influence jaw pain. Sleeping on one side or with pressure on the jaw may strain jaw muscles and joints. Poor neck and head alignment during sleep can also contribute to muscle tension and jaw discomfort.
How Can You Tell If Jaw Pain Is Serious?
Jaw pain may be considered serious if it is persistent, worsening, associated with swelling, numbness, difficulty opening the mouth, fever, or changes in bite. Pain following trauma or accompanied by facial asymmetry should be evaluated promptly.
What Is the 3 Finger Test for the Jaw?
The 3 finger test is a simple way to assess jaw opening. If you can comfortably fit three vertically stacked fingers between your upper and lower front teeth, your jaw opening is generally considered normal. Difficulty doing this may indicate restricted jaw movement.
Can You Survive Without a Mandible?
Survival without a mandible is possible with advanced medical care, but the mandible plays a critical role in eating, speaking, and facial structure. Reconstructive surgery is usually required to restore function and quality of life when part or all of the mandible is removed.
What Problems Affect the Mandible?
The mandible can be affected by fractures, infections, tumors, TMJ disorders, arthritis, osteonecrosis, and developmental abnormalities. Dental problems and chronic muscle tension can also indirectly impact mandibular health.
How Serious Is a Mandible Fracture?
A mandible fracture is considered a serious injury because it can affect breathing, chewing, speech, and facial symmetry. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications such as infection, malocclusion, or long-term functional problems.