Jaw clicking or popping sounds are commonly caused by temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, bruxism (teeth grinding), jaw trauma, disc displacement, arthritis, stress, and dental problems. These sounds typically occur while moving the jaw, especially during opening and closing. In many cases, the individual can hear the sound clearly, and in some situations, it may even be noticeable to others. Jaw clicking is a condition that should be treated with appropriate methods depending on its underlying cause.
What Is Jaw Clicking?
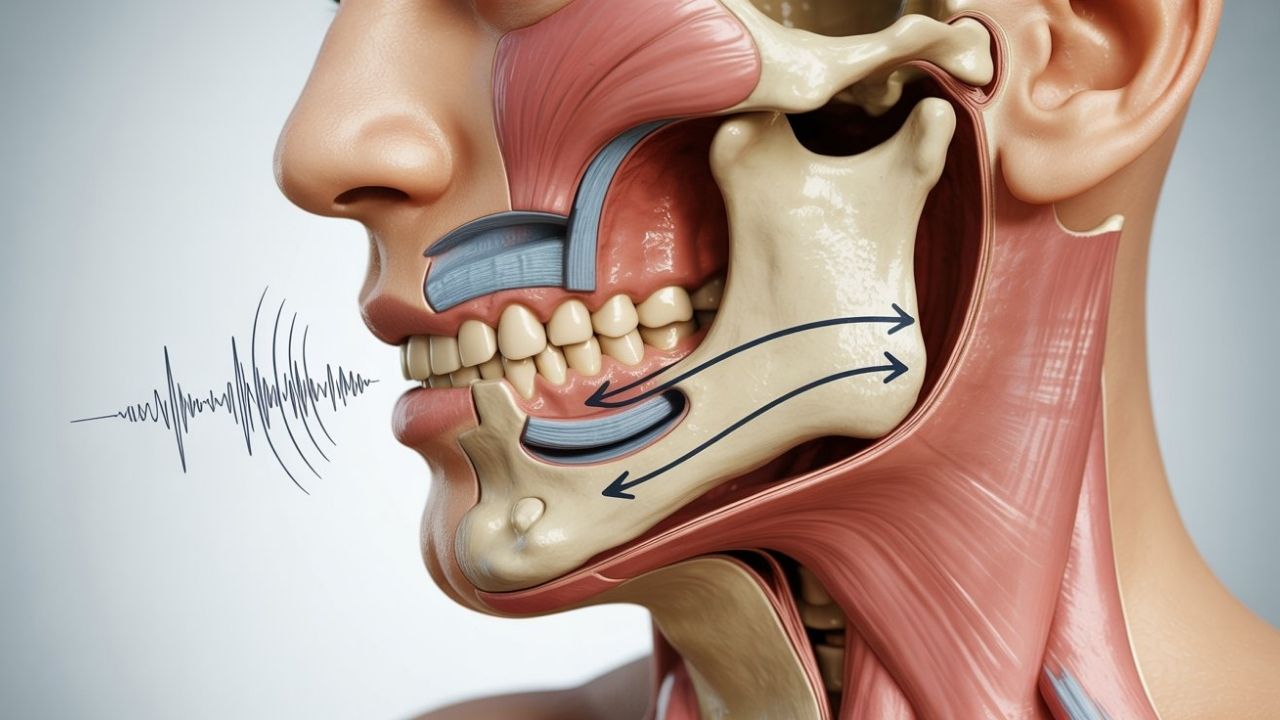
Jaw clicking is a condition most often associated with temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction. It may present as clicking, popping, cracking, grinding, or rubbing sounds. These sounds occur during jaw movements such as chewing, speaking, or opening the mouth.
For jaw sounds to be considered a medical issue, they must be persistent. Occasional or rare clicking usually does not indicate a serious problem. However, continuous jaw popping is often a sign of an underlying disorder and should be evaluated by a specialist as soon as possible.
Causes of Jaw Clicking
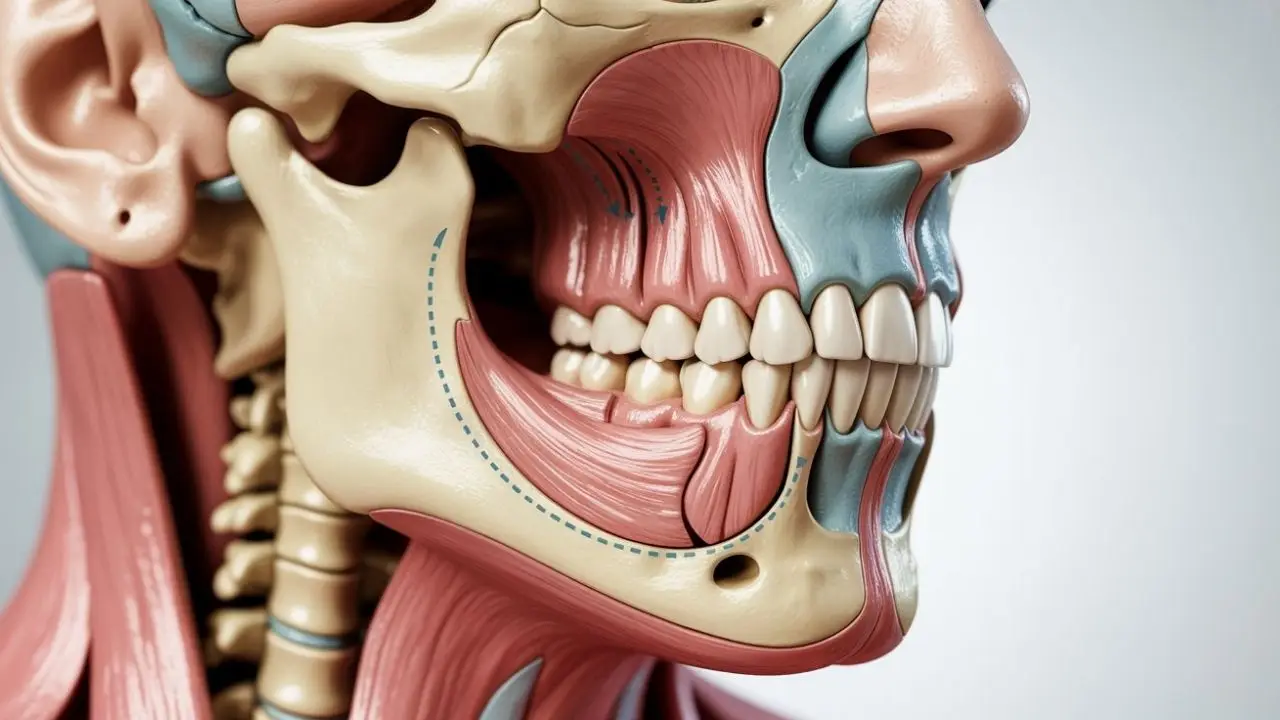
Jaw clicking can develop due to various factors. The most common causes include the following:
1 – Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
The lower jawbone (mandible) connects to the skull through the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This joint allows the jaw to move up, down, forward, and sideways. Problems affecting this joint are the most common causes of jaw sounds. TMJ-related issues that may lead to clicking include:
- Displacement of the joint disc
- Tension or spasms in the joint muscles
- Structural abnormalities that prevent normal joint function
It is important to note that these disorders do not always produce audible sounds.
2 – Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Bruxism is the involuntary clenching or grinding of teeth during sleep or throughout the day. This condition places excessive stress on the TMJ and causes muscle tension, making it a significant contributor to jaw clicking sounds.
3 – Jaw Trauma
Blows or injuries to the jaw can damage the TMJ, cause fractures, or overstretch the surrounding muscles. Such trauma can impair the normal function of the temporomandibular joint and lead to abnormal sounds.
4 – Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory joint disease that may develop due to aging or autoimmune conditions. When arthritis affects the TMJ, it can cause structural deterioration of the joint, leading to clicking and pain.
5 – Jaw Alignment Problems
Malocclusion, or improper bite alignment, places excessive load on the jaw joints and forces the muscles to work under constant stress. Over time, this negatively affects the TMJ structure and results in functional problems.
6 – Muscle Tension
Stress, excessive chewing, and poor posture can cause jaw muscles to become tense. Overstrained muscles interfere with joint mechanics and may contribute to clicking sounds.
In rare cases, conditions such as sinus infections or ear inflammation may also cause jaw-related noises.
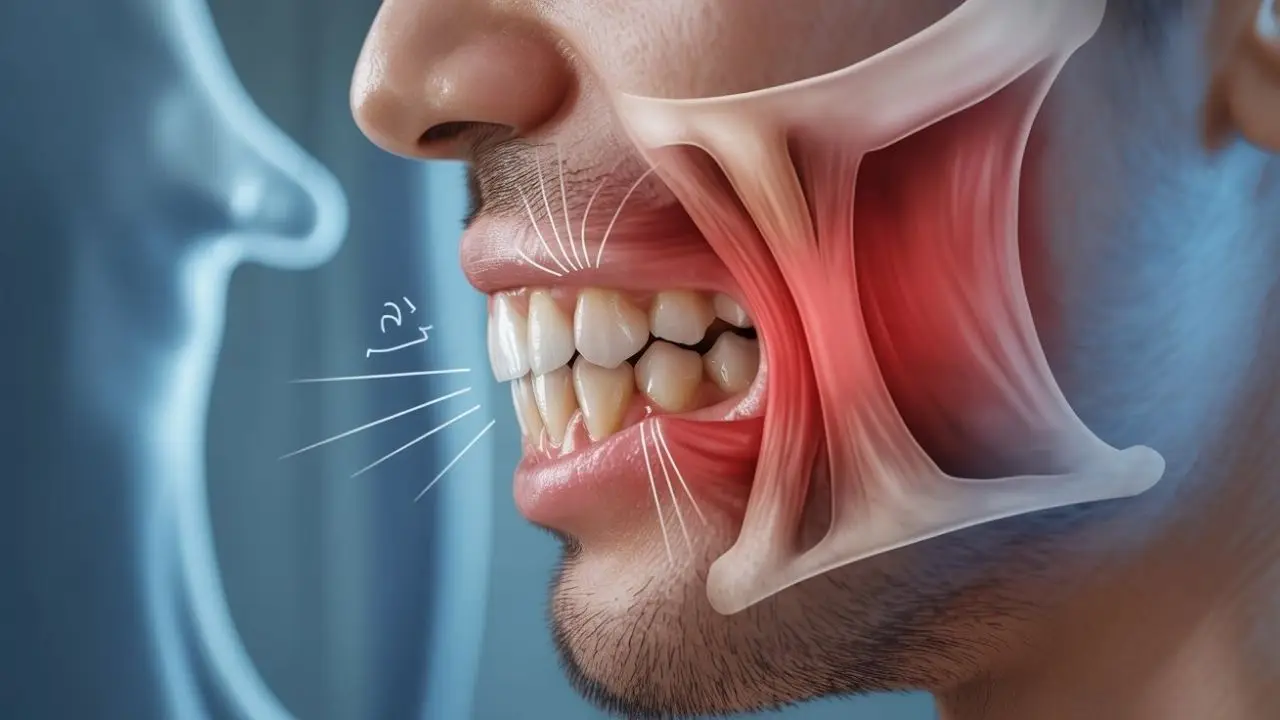
Diagnosis of Jaw Clicking When Opening the Mouth
Jaw clicking may be a symptom of serious underlying conditions, making accurate diagnosis essential. The diagnostic process typically includes the following steps:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | The patient’s symptoms are evaluated, and jaw movements are examined to identify when and how the sound occurs. |
| X-ray Imaging | X-rays may be used to assess the general structure of the jaw joint and surrounding bones. |
| CT Scan | Computed tomography provides detailed imaging of the joint’s bony structures. |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging offers detailed information about the condition of the joint disc and soft tissues. |
Blood tests may also be required if inflammatory conditions such as arthritis are suspected.
How Is Jaw Clicking Treated?
There are several treatment options for jaw clicking, and the choice depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment approaches include the following:
1 – Conservative Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of management for mild to moderate cases. Warm and cold compresses are used to relax muscles and reduce pain. Warm compresses help decrease muscle tension, while cold compresses are effective for pain control.
A soft-food diet is often recommended to minimize stress on the jaw joint. Medications may also be prescribed to relieve pain and reduce muscle tension.
2 – Dental Treatments
For cases caused by bruxism, night guards or splints are used to prevent teeth clenching and reduce stress on the TMJ.
If jaw clicking is related to dental alignment issues, orthodontic treatment may be recommended. These treatments typically last 12–18 months and aim to restore proper bite alignment.
3 – Surgical Methods
When conservative and dental treatments fail, surgical intervention may be considered as a last resort. Depending on the severity of the condition, advanced procedures such as artificial joint replacement may be required.
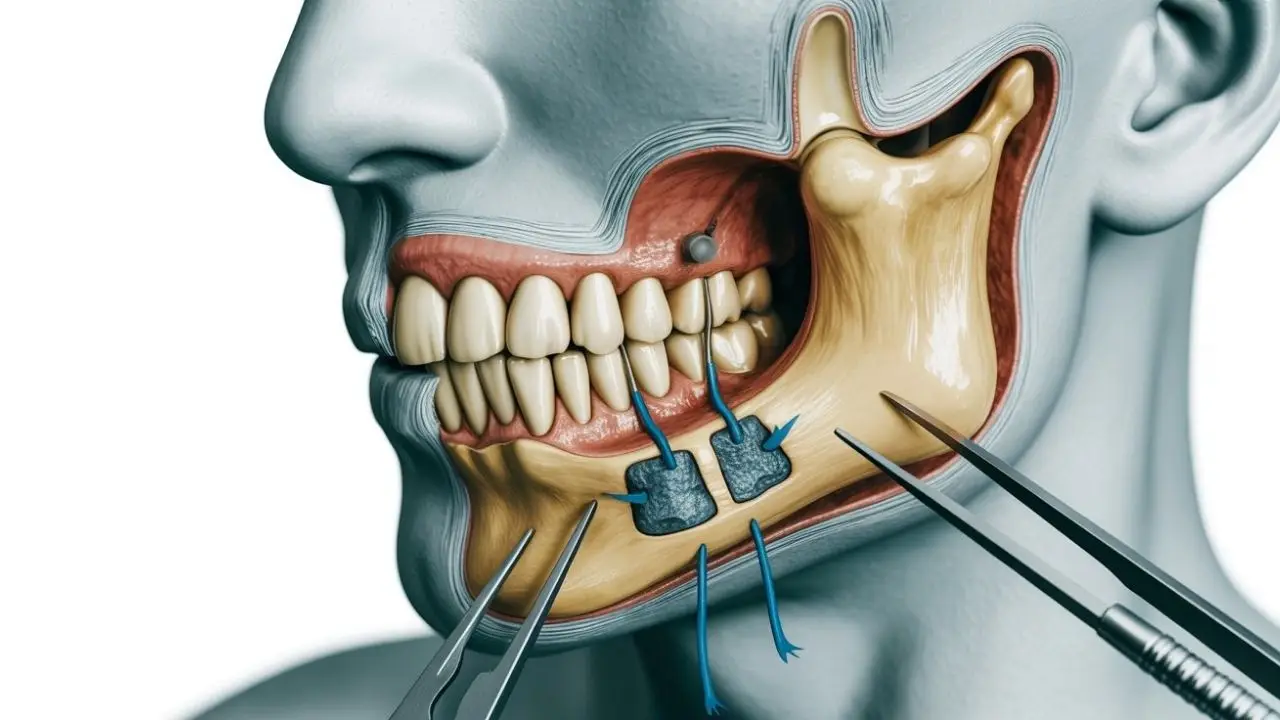
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Surgery
TMJ surgery is considered the final treatment option for jaw clicking and is generally recommended only when other methods have failed. If clicking occurs without pain or risk of joint damage, surgery may be postponed.
There are several types of TMJ surgical procedures, selected based on the patient’s condition:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Arthrocentesis | A minimally invasive procedure involving joint lavage to reduce intra-articular pressure and inflammation. |
| Arthroscopy | A camera-assisted surgical technique used to treat mild structural abnormalities and joint inflammation with a low risk of complications. |
| Discectomy | A surgical procedure involving removal of the temporomandibular joint disc, typically reserved for advanced or severe cases. |
TMJ surgery requires a high level of expertise, as even minor errors can lead to serious complications. Therefore, it should only be performed by experienced specialists.
Which Doctor Should You See for Jaw Clicking?
Patients experiencing jaw clicking should consult an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. These specialists receive advanced training in jaw surgery after completing dental school. If surgical intervention is necessary, an appropriate treatment plan is created; otherwise, patients may be referred to other relevant specialists.
Frequently Asked Questions About Jaw Clicking
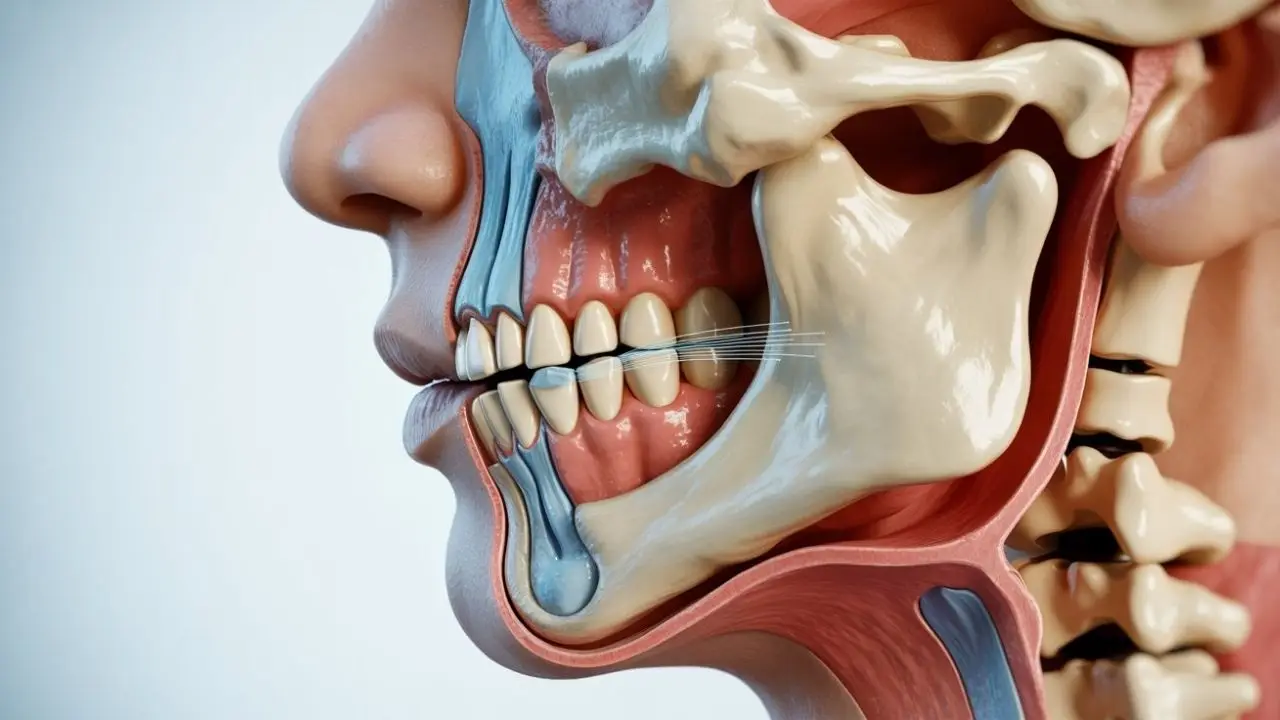
What Causes Jaw Clicking?
TMJ disorders are the most common cause. Other factors include dental misalignment, muscle tension, and bruxism.
My Jaw Clicks When I Open My Mouth. What Should I Do?
This sound is usually caused by TMJ problems. You should consult an oral and maxillofacial surgeon for proper evaluation.
How Is Jaw Clicking Treated?
Treatment typically begins with conservative methods such as exercises, compress therapy, and medication. Surgery may be considered if these methods fail.
Is Jaw Clicking a Serious Condition?
Jaw clicking can be a sign of serious underlying issues, especially if it is persistent. In such cases, professional evaluation is essential.
Is There Treatment for Jaw Clicking While Eating?
Jaw clicking and pain during eating are often related to TMJ disorders and can be treated with conservative therapies or surgical interventions when necessary.
How Do I Get My Jaw to Stop Clicking?
Jaw clicking can often be reduced by avoiding excessive jaw movements, eating soft foods, applying warm or cold compresses, managing stress, and avoiding habits such as teeth clenching or gum chewing. In persistent cases, treatment may include night guards, physical therapy, medication, or evaluation by a dentist or oral and maxillofacial specialist.
What Does It Mean If Your Jaw Clicks?
A clicking jaw usually indicates a problem with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), such as disc displacement, muscle imbalance, or joint inflammation. While occasional clicking may be harmless, frequent or painful sounds often signal an underlying TMJ disorder.
What Is the 3 Finger Test for TMJ?
The 3 finger test is a simple self-assessment for jaw mobility. If you can comfortably place three vertically stacked fingers between your upper and lower front teeth when opening your mouth, your jaw opening is generally considered normal. Difficulty doing so may indicate TMJ dysfunction.
Can TMJ Clicking Go Away on Its Own?
Yes, mild TMJ clicking without pain can sometimes resolve on its own, especially if caused by temporary muscle tension or minor disc displacement. However, persistent clicking, worsening symptoms, or pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Jaw Clicking?
Vitamin deficiencies do not directly cause jaw clicking, but deficiencies in vitamin D, magnesium, or B-complex vitamins may contribute to muscle weakness, inflammation, or nerve-related symptoms that can aggravate TMJ problems.
Are Clicky Jaws Common?
Yes, jaw clicking is relatively common. Many people experience occasional clicking or popping without pain or functional limitation. Only a smaller percentage develop symptomatic TMJ disorders requiring treatment.
What Are the Early Signs of TMJ?
Early signs of TMJ disorders include jaw clicking or popping, jaw stiffness, facial or ear pain, headaches, difficulty chewing, and limited or uneven jaw movement. Symptoms may worsen with stress or excessive jaw use.
Can a Dentist Help With TMJ?
Yes, dentists—especially those trained in TMJ disorders—can help diagnose and manage TMJ problems. Treatments may include bite splints, night guards, bite adjustment, and referral to specialists when necessary.
What Are the Facial Signs of B12 Deficiency?
Facial signs of vitamin B12 deficiency may include pale or yellowish skin, mouth ulcers, tongue inflammation (glossitis), facial numbness or tingling, and in some cases muscle weakness that can affect facial and jaw muscles.
What Are 5 Physical Signs You’re Taking Too Much Vitamin D?
Excessive vitamin D intake may cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, frequent urination, excessive thirst, muscle weakness, bone pain, and confusion. These symptoms are usually related to elevated calcium levels in the blood.
Can Dehydration Cause Jaw Clicking?
Dehydration does not directly cause jaw clicking, but it can contribute to muscle fatigue, cramping, and reduced joint lubrication, which may worsen existing TMJ symptoms or make jaw noises more noticeable.