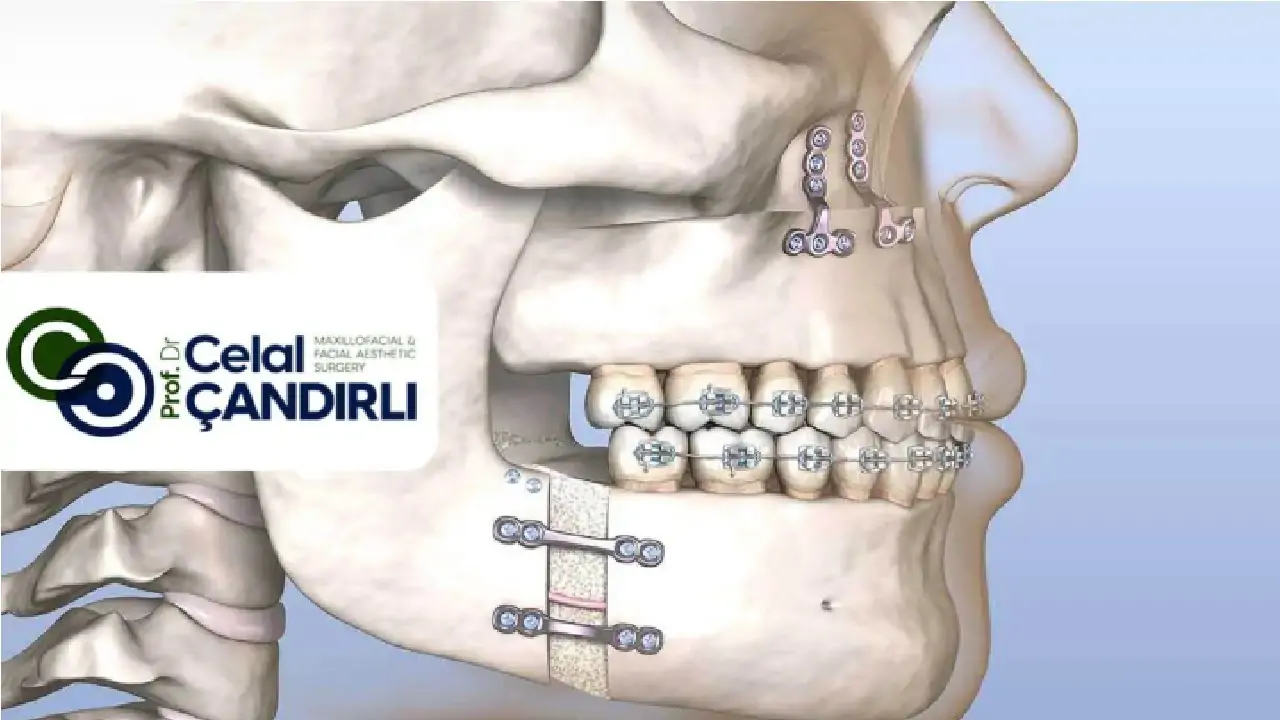
Orthognathic surgery for TMJ (temporomandibular joint) is performed to permanently treat disorders occurring in the jaw joint. Various options tailored to the specific joint problem are available, and the appropriate option is selected based on the patient’s condition.
Orthognathic surgery for TMJ is an effective option, but conservative (non-surgical) treatments are typically attempted first. When joint disorders do not improve with conservative treatments, surgical methods are considered.
What Are Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders?
The temporomandibular joint allows movement of the lower jaw. Thanks to its unique structure, the jaw moves side to side and up and down, facilitating essential functions such as speaking, chewing, and swallowing. However, discomfort in this joint can restrict movement and lead to various issues, which is when orthognathic surgery for TMJ may be necessary.
Common TMJ disorders include:
- Ankylosis (loss of movement due to joint stiffening)
- Inflammatory diseases such as capsulitis, arthritis, and synovitis
- Dislocation (spontaneous dislocation)
- Subluxation
- Problems with the joint surface (adhesions, shape distortions, etc.)
- Integrity loss of the condylar disc
- Developmental and congenital defects
- Disc displacement
- Degeneration (osteoarthritis)
- Jaw protrusion
- Nerve disorders
These issues often lead to facial asymmetry. If orthodontic specialists cannot treat this asymmetry, orthognathic surgery becomes necessary.
The severity of TMJ disorders varies among patients. In some cases, conservative treatments and lifestyle changes are sufficient to alleviate discomfort. In more severe cases, orthognathic surgery for TMJ is preferred.
Symptoms of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
TMJ disorders manifest through various symptoms, which include:
| Symptoms | Description |
| Pain | The most common symptom, occurring in the joint and surrounding muscles, which can happen during stillness or while chewing and speaking. |
| Restricted Movement | Limited opening and closing of the jaw, with potential for jaw locking. |
| Sounds | Friction sounds during jaw movement, often heard as clicks or pops. |
| Ear Pain | Proximity of the TMJ to the ear can cause ear pain. |
| Swelling | Swelling may occur in the joint area or the face. |
| Difficulty Functioning | Challenges in chewing, speaking, and swallowing. |
Conservative treatment methods are first employed for these symptoms. If there is no improvement, orthognathic surgery may be considered. However, non-surgical methods should always be prioritized, as orthognathic surgery for TMJ requires significant expertise.
Prof. Dr. Celal Candirli, who has extensive experience in orthognathic surgery procedures, can help manage these disorders. Feel free to contact us for more information about TMJ surgery.
Orthognathic Surgery Methods for TMJ
Orthognathic surgery for TMJ addresses joint problems to alleviate or treat them. The TMJ, connecting the jawbone and skull, is essential for functions like speaking and chewing. Not every disorder requires surgical intervention; sometimes orthodontic treatments or lifestyle changes are sufficient. Orthognathic surgery for TMJ is typically preferred in cases of:
- Jaw locking
- Painful dysfunction
- Disc disorders
- Calcification in the jaw joint
Various procedures exist for addressing TMJ disorders, including:
- Arthrocentesis
A minimally invasive method preferred for simple cases, using local anesthesia. Sterile needles inject special fluids into the jaw joint to cleanse toxins and harmful substances. Recovery time is very short, allowing patients to return to their daily routines the same day. - Arthroscopy
Used for both diagnosis and treatment, a small incision is made in the joint area to insert a camera. The images guide correction of disc displacements, release adhesions, and reduce inflammation. This procedure causes minimal tissue damage and has a short recovery time, making it suitable for mild disc displacements and adhesions. - Diskectomy
Performed when the joint disc loses its function, this involves removing the disc and replacing it with a synthetic one. In some cases, tissue from the patient is used as a replacement. This method is chosen for severe disc damage and displacements. - Total Joint Prosthesis
This procedure involves completely replacing the TMJ, typically used in cases of degeneration and severe damage. The disc and other structures are entirely removed and replaced with titanium and synthetic materials. This option is comprehensive for addressing serious joint issues and restoring jaw function.
These procedures specifically target TMJ disorders. Other treatments, such as orthognathic surgery and braces, address jaw irregularities and dental alignment issues.

How Is Jaw Joint Surgery Performed?
Orthognathic surgery for TMJ includes various procedures, each with different steps and methods of application. Depending on the procedure, patients may receive local or general anesthesia. A small incision is then made to access the joint, usually from inside the mouth or another suitable area. Necessary interventions are conducted through this incision, and the joint issues are corrected with prosthetics or other methods. Finally, the incisions are closed, completing the procedure.
Post-surgery, patients may be discharged on the same day or kept under observation for a few days, depending on the procedure. Regular follow-ups are essential.
Risks of Temporomandibular Joint Surgery
Despite its effectiveness, temporomandibular joint surgery carries some risks, including:
- Swelling and bruising
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Healing issues at the incision site
- Need for revision surgery
- Jaw alignment discrepancies
- Unwanted fractures
These risks can be minimized through the selection of an experienced surgeon, significantly reducing the chances of complications.
Prices for Orthognathic Surgery for TMJ
Prices for orthognathic surgery for TMJ vary based on the procedure performed. Factors such as the doctor’s experience, clinic pricing policies, and location are important considerations. Given that these procedures require serious expertise, priority should be given to surgical experience rather than just cost. For more information about TMJ surgical methods and pricing, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Orthognathic Surgery for TMJ
Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers:
1 – How is Orthognathic Surgery for TMJ Performed?
Depending on the method used, either closed or open surgery may be performed. Local or general anesthesia is administered based on the procedure, followed by an incision to access the joint and correct the issues.
2 – What Causes TMJ Disorders?
Factors such as teeth grinding, one-sided chewing, trauma, missing teeth, tumors, genetic factors, congenital anomalies, and prolonged postural issues can lead to TMJ disorders.
3 – What is TMJ Surgery?
Also known as orthognathic surgery for TMJ, this procedure aims to address disorders in the jaw joint and includes various interventions, including complete joint replacement.
4 – How Can an Asymmetric Jaw Be Corrected?
Conservative treatments and orthodontic methods are used for asymmetric jaws. If these do not yield results, orthognathic surgery for TMJ is considered.
5 – In Which Situations is Orthognathic Surgery for TMJ Preferred?
It is chosen for conditions like jaw locking, painful dysfunction, calcification in the joint, and disc disorders.